Why Is Stem Cell Therapy a Hot Topic in Medicine?
Stem cells can develop as brain, muscle, and other cell types. They are fundamental for regenerative medicine to heal injured tissues and investigate treatments for spinal cord injuries, diabetes, and Parkinson’s disease. The great promise and ethical and scientific difficulties of stem cell therapy are highlighted by both benefits and drawbacks of these cells. Benefits are revolutionary medical discoveries and the potential of treating once untreatable diseases; drawbacks are embryonic stem cell research, cost, and long-term safety. Talking about the advantages and drawbacks guarantees moral, creative ideas and responsible stem cell research.
Stem cell research came from scientists learning in the middle of the 20th century the regenerative properties of bone marrow cells. Separating mouse embryonic stem cells in 1981 opened the avenue for later investigation. Late 1990s saw the isolation of human embryonic stem cells, therefore facilitating regenerative medicine. To address ethical issues raised in stem cells pros and cons debates, researchers generated induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) as a substitute for embryonic cells. From organ regeneration study to bone marrow transplants for blood disorders, these developments have considerably expanded stem cell treatments. Though the subject has developed rapidly, appropriate stem cell technology development depends on careful evaluation of advantages, risks, and ethical consequences of amniotic stem cells facts.
Stem cell conflicts influence public perspective and policy decisions on moral, medical, and social concerns. Embryonic stem cells are divisive since some think they ruin human life while others think they help to propel medical progress. Though risks, safety, and long-term repercussions still exist, stem cells show immense promise to heal damaged tissues and treat incurable diseases. Social dialogues, however, draw attention to stem cell therapy equity so that advancements are not limited to affluent populations. Public attitudes, hope, and skepticism have all been formed by discussions on stem cells pros and cons, which still have an impact on funding decisions and regulatory frameworks around the world.
How Stem Cell Therapy Works
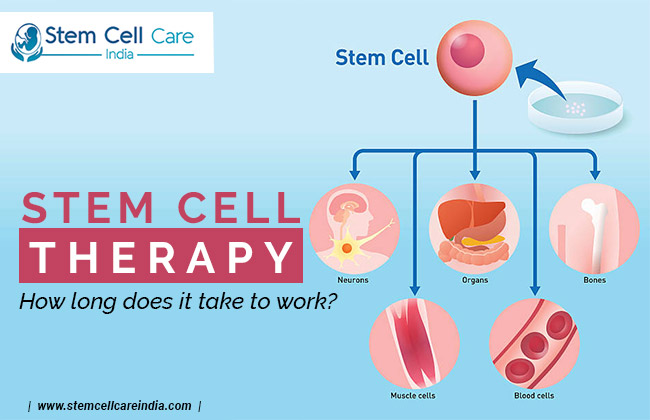
Because stem cells can develop into many kinds of specialized cells, they are rather important in medicine. Main groups are embryonic, adult, and induced pluripotent stem cells. Although practically any cell type may be produced from early-stage embryonic stem cells, its use raises ethical questions. Found in bone marrow, adult stem cells are less flexible but ethically sound with few applications. Made from reprogramming adult cells, iPSCs represent a possible and moral substitute for embryonic stem cells. Though immunological rejection, ethical concerns, and technology challenges still exist, stem cells have the ability to transform cancer, diabetes, and spinal cord injury treatment.
Using their special properties, stem cell treatment heals, replaces, and rejuvenates damaged organs and tissues. Normal is separating stem cells from a donor or patient, cultivating them in a lab, and then moving them to a damaged or diseased location. These cells can rebuild tissue to heal or become neurons, muscle cells, or blood cells. Released by stem cells, growth elements help the body to naturally heal and lower inflammation. Stem cells pros and cons must be carefully weighed, notwithstanding their ability to treat degenerative diseases and undo tissue damage. Technical intricacy, immunological rejection, and poor targeting stop broad application.
The Benefits of Stem Cell Therapy
Revolutionizing Modern Medicine
Medical advances in stem cells pros and cons research have changed how we treat previously untreatable illnesses. Stem cell therapy for spinal cord injuries and regenerative heart disease treatments have showed promise in repairing damaged tissues. Stem cells can differentiate into numerous cell types, allowing organ and tissue repair and regeneration—a fundamental benefit of this research. However, embryonic stem cell utilization raises ethical considerations and makes long-term safety and efficacy difficult. Stem cell research has great potential for individualized therapy and health issues, despite these obstacles.
Personalized Treatment Options
Stem cells provide personalized medical therapies for each patient. Weighing stem cells pros and cons, the pros include tailored illness management, which reduces the chance of negative effects from broad, non-specific treatments. Stem cells can rebuild tissue destroyed by Parkinson’s disease or diabetes, providing immediate treatment. Individual patient biology might cause unanticipated results, making it difficult to ensure these highly customized medicines are safe for long-term usage. Despite these obstacles, stem cells’ potential to transform tailored treatment drives research and innovation.
Faster Recovery and Healing
Stem cells accelerate healing from injuries and degenerative diseases, altering the way we treat them. Stem cells can develop into numerous cell types, allowing them to repair cartilage, bones, and heart muscle. Case studies show that stem cells can recover some motor function in severe spinal cord injury patients. Clinical investigations with cardiac patients have revealed that stem cells in damaged areas increase heart function. Despite these encouraging results, these regenerative therapies must be rigorously tested to avoid consequences like excessive cell development or immune system rejection. These stem cells pros and cons must be balanced as researchers develop safer and more effective recovery treatments.
The Challenges and Risks of Stem Cell Therapy
Cost of Stem Cell Therapy
Since stem cell technology is still growing, cost and accessibility are major challenges. The high expense of these therapies can prevent low-income people from accessing them, creating a healthcare gap. Due to global cost differences, low-income people may have even more trouble getting care. Stem cells may improve medical treatments, but their high cost and unequal distribution of resources suggest that more economical and inclusive techniques are needed to ensure benefits are available to all.
Ethical Concerns
Embryonic stem cells are at the nexus of medical innovation and ethical issues, sparking heated arguments. While stem cells pros and cons are debated, supporters highlight embryonic stem cells’ potential to treat terminal diseases. Critics say the destruction of human embryos raises profound moral and philosophical problems about existence. Induced pluripotent stem cells are being discussed as a way to address ethical concerns without slowing scientific progress while advancing life-saving technologies.
Potential Side Effects and Complications
Despite their potential, stem cell therapies have hazards, adding to the stem cells pros and cons discussion. Immune rejection, where the recipient’s body assaults transplanted stem cells, can cause problems or treatment failure. Rapid stem cell division and differentiation can cause uncontrolled tumor development. Stem cell collection, processing, and implantation can lead to infection. These dangers emphasize the necessity for long-term research to evaluate stem cell-based therapies’ safety and efficacy to ensure patient safety. Researchers and doctors must weigh these risks and rewards.
Current Applications of Stem Cell Therapy
Stem cell therapy is promising for treating chronic diseases like diabetes, arthritis, and neurological diseases like Parkinson’s and Alzheimer’s. This therapy uses stem cells to heal tissues and restore functions. In diabetes, stem cells can repair insulin-producing cells, lowering insulin reliance. Stem cells also regenerate cartilage in arthritis to relieve pain and increase mobility. While stem cell therapy has the promise for focused healing and long-term advantages, it also has drawbacks such high costs, ethical issues about stem cell sources, and the possibility of immune rejection or tumor growth. These factors influence the development and availability of this unique medical technology.
Stem cells for hair and skin rejuvenation show how beauty and medicine meet. Stem cells are used to repair and regenerate skin, minimize aging, and stimulate hair follicles to prevent hair loss. Stem cells can develop into various cell types and encourage healing, providing a natural cosmetic solution. These stem cells pros and cons include their ability to restore skin and scalp health without surgery and deliver long-lasting results. These medicines require more investigation and ethical issues due to high prices, restricted accessibility, and long-term effectiveness concerns.
Weighing the Pros and Cons
Medical professionals are interested in stem cell therapy due to its potential benefits and drawbacks. Stem cells can rebuild damaged tissues, enabling new treatments for spinal cord injury, diabetes, and heart disease. They can also differentiate into numerous cell types, making them useful for medical research. However, stem cells pros and cons must be considered. Ethics, especially embryonic stem cells, remain controversial. High costs and restricted availability can limit therapy access, and some medicines’ long-term consequences are unknown. Weighing the pros and cons of stem cells underlines the need for continued research and balanced conversations to maximize their potential while addressing issues.
Ask your doctor informed questions about stem cell therapy to make evidence-based decisions. Start by discussing the illness you want to cure and whether the therapy works. Ask about the procedure’s dangers, benefits, and long-term effects, considering stem cells pros and cons. Understanding the source and kind of stem cells—adult, embryonic, or induced pluripotent—is also crucial. Ask the clinician about stem cell treatment experience and assess clinical data for the recommended technique. A thorough discussion assures a selection based on trustworthy research and your medical needs.
Write and Win: Participate in Creative writing Contest & International Essay Contest and win fabulous prizes.