Garden Photo : genengnews.com
This recent development has rightfully made headlines all over the world: stem cells can be harvested from a person’s cheek cells, creating this revolutionary discovery. Now scientists are working to create human organs using these tissues.
Stem cells have been a hot topic for quite some time now, but with such great growth in their potential, it is important to know what exactly they are and how they work as well as what the consequences of their usage could be.
Stem cells are those that could regenerate, and their sources are the cells that make up the tissues. Even though it is too early to state how they work, scientists believe stem cells can also repair damaged and diseased tissues.
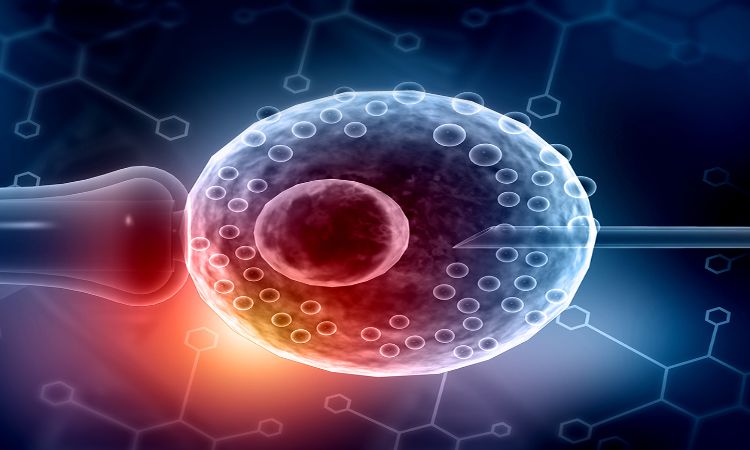
Stem cells are used in a range of cell therapies to repair tissues and organs, regenerate immune systems, treat cancer, and more. They can be derived from both adults and foetuses . Embryonic stem cells have the potential to form all the different types of cells in an early embryo and allow it to develop into any cell type found in that organism; these could theoretically be used for regenerating tissues or organs damaged by disease or injury.
The stem cells commonly used in research at this current point in time are the induced pluripotent stem(iPS) cells type (a type of somatic cell that is converted into a pluripotent state in vitro)and embryo-derived ones. Human embryonic stem cells (HESCs) can be derived from the inner cell mass of human embryos, destined to become humans. HESCs have been used in research as well as being sold as a treatment for certain diseases such as Parkinson’s disease and Alzheimer’s disease.
The United Kingdom has been a leader in regenerative medicine since work by Sir Martin Evans on embryonic stem cells was used to develop techniques to derive stem cells from other sources. Since then, other individuals and teams have developed different ways of deriving stem cells. The first team to use iPS cells was Shinya Yamanaka’s team at Kyoto University. They achieved this by introducing four genes (Oct-4, Sox2, Klf4, and c-MYC), in combination with a factor called Oct3/4 into human somatic cells. They then found that these induced pluripotent stem cells had characteristics of embryonic stem cells and could be grown into tissue that was identical to the tissue of embryos. Yamanaka received the Nobel Prize for this work in 2014.
There is quite a lot of research being done on stem cells currently, however, there is still much to be done for us to fully understand the way stem cells function in the human body. Moreover, there are some controversies with stem cell usage, such as timing and how they should be used. According to the American Medical Association, using human embryos for research is unethical and should be illegal. In 2001 the United Nations General Assembly adopted a declaration prohibiting human cloning, including of embryos.
Despite the controversies, Stem cells are known to be responsible for repairing and regenerating tissue in humans and animals. Stem cell therapy is a process of treatment that involves the injection of stem cells into an injured area. The goal is to reprogram the cells so they can self-regenerate their ability to destroy diseases or heal injured tissue.
The practice of applying stem cell therapy is new in the United States but has enjoyed more widespread use in other parts of the world. Most notably, stem cell therapy is being used to treat patients with type 1 diabetes. The procedure involves isolating specific embryonic or adult stem cells from a patient’s bone marrow and then transforming these stem cells into islets. These newly converted islet cells are then transplanted back into the patient’s pancreas where they restore insulin production to its normal state.
In recent years, this technology has been applied to several medical treatments related to bone marrow transplantation, spinal cord injuries, burns, as well as many others.Consumers are not only living longer and better lives, but their sense of self is becoming stronger. Part of this is due to a newfound appreciation for emerging technologies that have the power to help them maintain their quality of life.
A potential future benefit of stem cell treatments is the possibility of anti-aging treatments. In fact, stem cell treatments are already being used to treat aging. For example, studies using iPS cells have shown that these cells can produce new brain cells, and thus may treat conditions like Alzheimer’s disease. Additionally, researchers at the University of Texas Medical Branch in Galveston showed that neural stem cells could be used to treat stroke patients with damaged blood vessels.
On a different note, stem cell treatments might also help people with mental health issues like anxiety or depression. A recent study showed that stem cells can be used to treat depression by increasing the number of neurons in the hippocampus.
While stem cell treatments are becoming more routine, there is an even more innovative possibility on the horizon. This is nanotechnology—the manipulation of matter at an atomic or molecular level and its use in stem cell treatments. To this end, scientists have already developed many nanoscale materials for medical use.Although there are many challenges ahead before stem cell treatments can become commonplace both in research and in clinical settings there is no doubt that this technology will play a significant role in the healthcare industry over the next few decades.
By DIVYA HEMBROM, BANGALORE